Changes of Phase
Matter exists in different forms known as phases, or states, which describe how particles are arranged and how they move. The most familiar phases are solid, liquid, and gas, though plasma is also a common phase found in stars and lightning. In a solid, particles are tightly packed and vibrate in place, giving the object a fixed shape and volume. Liquids have particles that are close together but can slide past one another, allowing liquids to flow and take the shape of their container. Gases have particles that are far apart and move freely, so they expand to fill any space. These phases are not permanent, and matter can change from one phase to another under certain conditions.
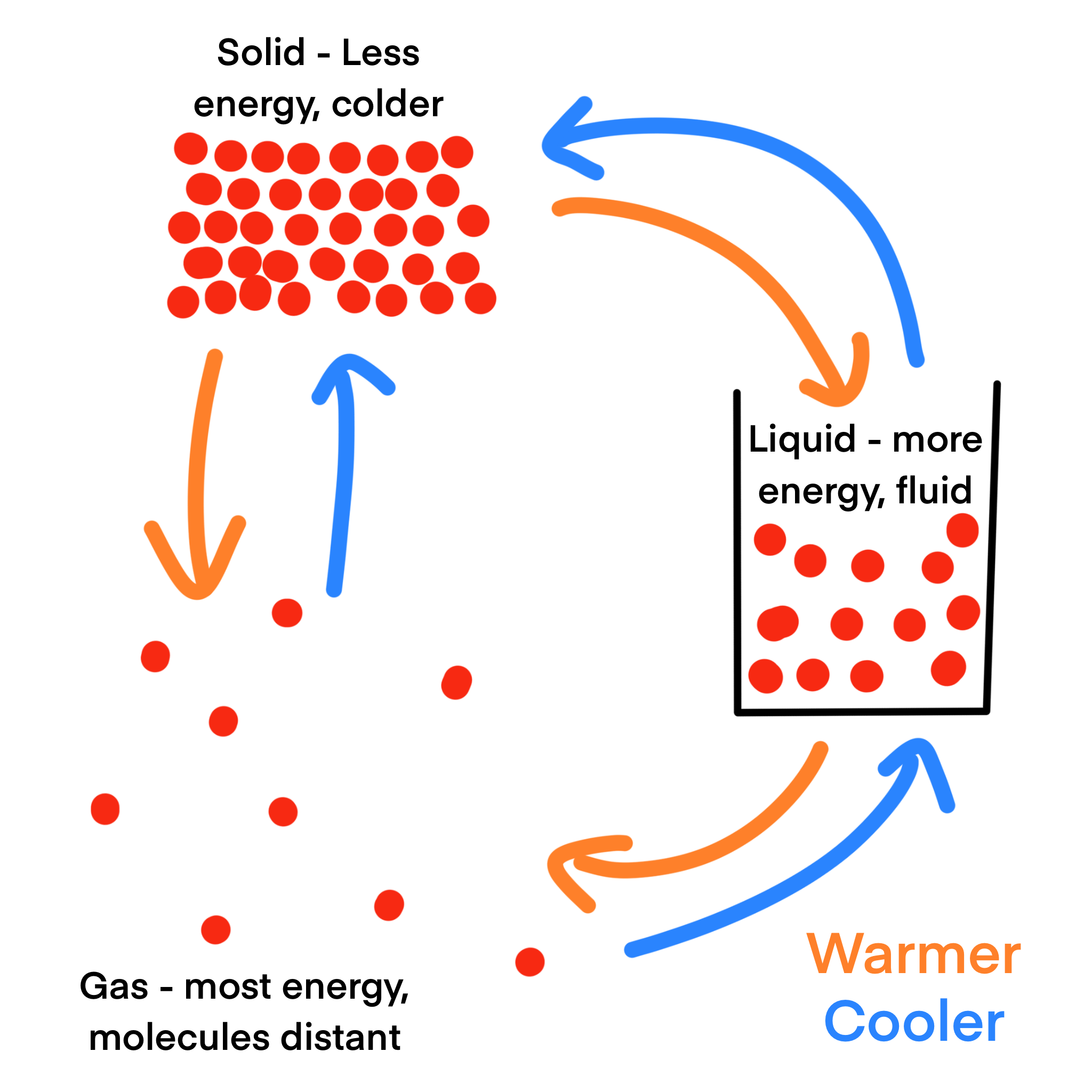
The Role of Temperature and Energy
Temperature plays a major role in phase changes because it reflects the amount of energy particles have. When heat energy is added to a substance, its particles move faster and spread farther apart. This increased motion can cause a solid to melt into a liquid or a liquid to evaporate into a gas. When heat is removed, particles lose energy, slow down, and move closer together, causing gases to condense into liquids or liquids to freeze into solids. During a phase change, the temperature of a substance often stays the same while energy is being used to rearrange the particles rather than increase their speed.
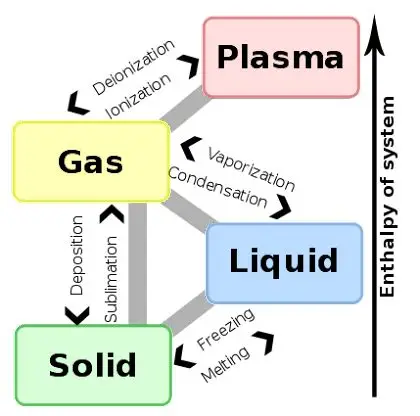
Common Phase Changes Explained
There are several types of phase changes that occur in everyday life. Melting happens when a solid absorbs energy and becomes a liquid, such as ice turning into water. Freezing is the opposite process, where a liquid loses energy and becomes a solid. Evaporation occurs when a liquid changes into a gas, often at the surface, while boiling is a faster form of vaporization that happens throughout the liquid. Condensation occurs when a gas loses energy and becomes a liquid, like water droplets forming on a cold glass. Some substances can change directly between solid and gas without becoming liquid, a process called sublimation, while the reverse process is known as deposition.
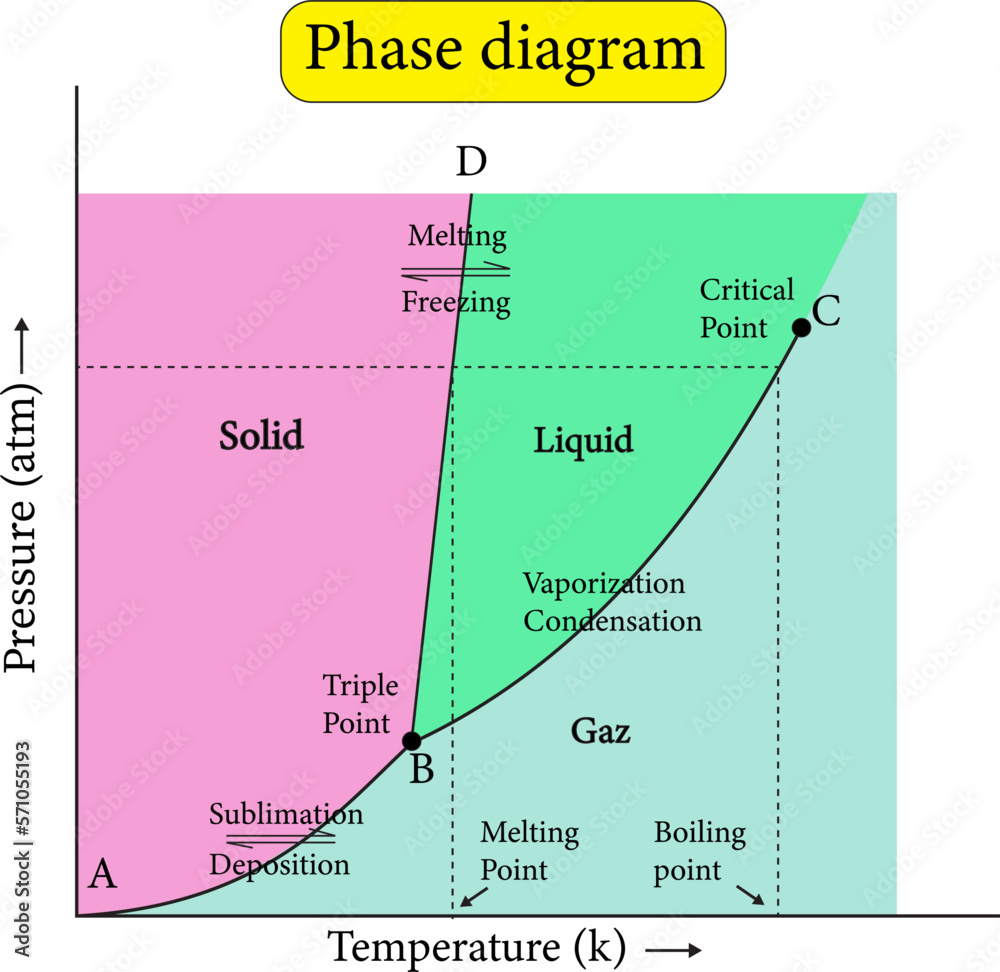
The Role of Pressure in Phase Changes
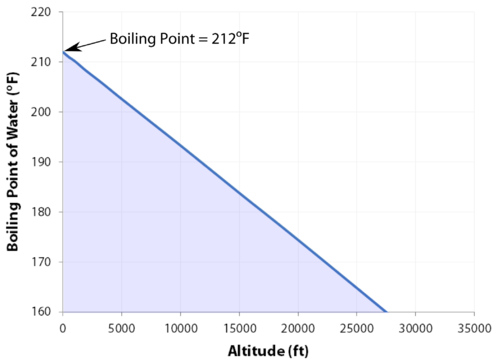
Pressure also affects how and when phase changes occur. Pressure is the force exerted by particles when they collide with surfaces or each other. Increasing pressure can push particles closer together, making it easier for gases to turn into liquids or liquids into solids. Decreasing pressure allows particles to spread out more easily, which can lower the temperature at which a substance boils. For example, water boils at a lower temperature at high altitudes because the air pressure is lower. This shows that phase changes depend not only on temperature but also on the surrounding environment.
Why Phase Changes Matter in Everyday Life
Phase changes are important because they affect many natural and human-made processes. Weather patterns rely on evaporation and condensation to form clouds and precipitation. Cooking involves melting, boiling, and evaporation, such as melting butter or boiling water. Refrigerators and air conditioners work by controlling phase changes to remove heat from enclosed spaces. In nature, phase changes help regulate Earth’s temperature and water cycle. Understanding how matter changes phase helps explain many everyday phenomena and supports advancements in science and technology.

